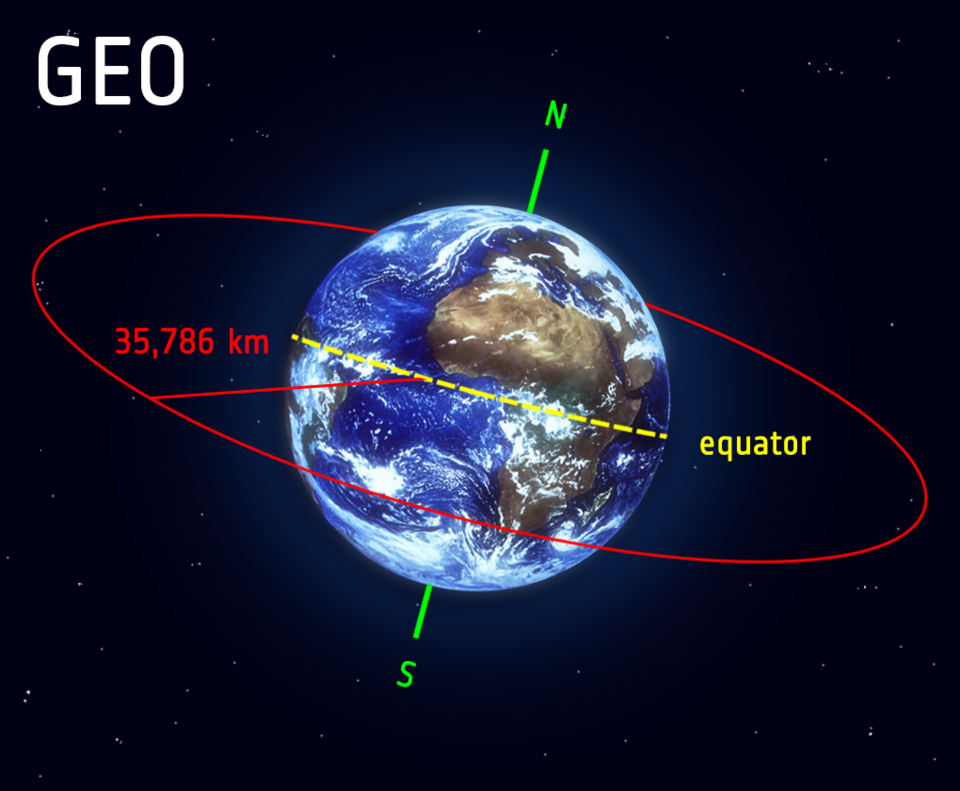
- A geostationary orbit (or Geostationary Earth Orbit - GEO) is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator (0° latitude), with a period equal to the Earth's rotational period and an.
- Earth from Geostationary Orbit. Northrup Grumman’s MEV-1 satellite captured this view of Intelsat 901 on February 25, 2020. Credit: Northrup Grumman. Lots of satellites are in geostationary orbit around Earth. But last year, Northrup Grumman made history not only by performing the first docking of two commercial satellites to demonstrate on.
- Videos For Geostationary Earth Orbit
- Geostationary Satellite Orbit, GEO - Electronics Notes
- See Full List On Gravity.wikia.org
- Geostationary Orbit Earth Radius
Videos For Geostationary Earth Orbit
One particular form of geosynchronous orbit is known as a geostationary orbit. In this type of orbit the satellite rotates in the same direction as the rotation of the Earth and has an approximate 24 hour period.

Geostationary Satellite Orbit, GEO - Electronics Notes

See Full List On Gravity.wikia.org
Geostationary Orbit Earth Radius
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь. 2001.
Смотреть что такое 'earth-centered orbit' в других словарях:
Orbit — This article is about orbits in celestial mechanics, due to gravity. For other uses, see Orbit (disambiguation). A satellite orbiting the Earth has a tangential velocity and an inward acceleration … Wikipedia
Molniya orbit — For other uses, see Molniya (disambiguation). Figure 1: The Molniya orbit. Usually the period from perigee + 2 hours to perigee + 10 hours is used to transmit to the northern hemisphere Molniya orbit is a type of highly elliptical orbit with an… … Wikipedia
Apollo 15, Return to Earth — After the Apollo 15 Lunar Module Falcon lifted from the lunar surface it rendezvoused and docked with the Command/Service Module Endeavour . After transferring across the lunar samples and other equipment, Falcon was jettisoned. It would fire its … Wikipedia
Geostationary orbit — Geostationary orbit.To an observer on the rotating Earth (fixed point on the Earth), the satellite appears stationary in the sky. A red satellite is also geostationary above its own point on Earth. Top Down View … Wikipedia
History of the Earth — For the history of modern humans, see History of the world. Geological time put in a diagram called a geological clock, showing the relative lengths of the eons of the Earth s history The history of the Earth describes the most important events… … Wikipedia
Expanding Earth theory — The Expanding Earth theory is an attempt to explain the position and movement of continents (continental drift) on the surface of the Earth. The expanded earth theory (and plate tectonics) incorporates the appearance of new crustal material at… … Wikipedia
When We Left Earth: The NASA Missions — DVD/Blu ray case Genre Documentary, science, space exploration, historical Narrated by … Wikipedia
Timeline of astronomy — Timeline of astronomy2500 BCMany ancient sites are thought to have astronomical significance, such as the Ancient Egyptian pyramids, Harappan shell instruments, British megaliths, and buildings in China and Latin America.In Lothal, the ancient… … Wikipedia
Mars — This article is about the planet. For other uses, see Mars (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
Apollo 15, Outward journey — Launching at 9:34:00 am EST on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 would take four days to reach the Moon. After spending two hours in orbit around the Earth, the S IVB third stage of the Saturn V was reignited to send them to the Moon.During the retrieval… … Wikipedia
Deferent and epicycle — Deferent redirects here. For the acknowledgement of the legitimacy of the power of one s superior or superiors, see Deference. The basic elements of Ptolemaic astronomy, showing a planet on an epicycle (smaller dashed circle) , a deferent (larger … Wikipedia
